In the evolving landscape of decentralized identity, there are a multitude of challenges that must be addressed to fully harness its potential. While decentralized identity holds the promise of empowering individuals with greater control over their personal data and enhancing privacy, it is not without its hurdles. In this blog post, we will delve into the challenges faced by decentralized identity systems and explore potential solutions to tackle them effectively.
Standardization
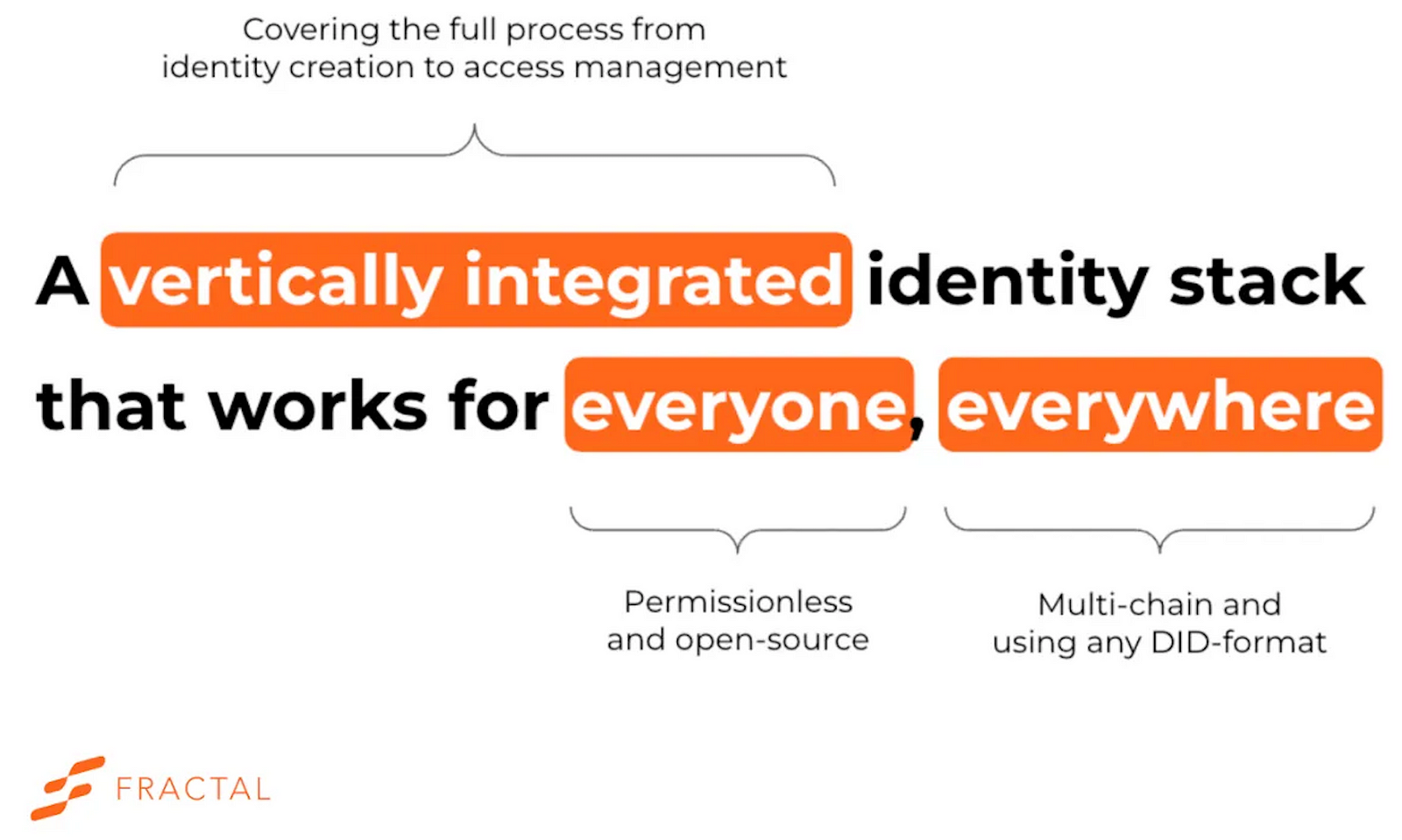
The benefits of having a decentralized identity that represents a single version of the truth can only be realized if it is accepted by all organizations, governments, and other ecosystems. In turn, this depends on achieving standards for issuing, holding, and verifying DIDs such that all credentials are verified, trustworthy, and securely stored and transferred.
For instance, passports are issued based on international standards that make them acceptable credentials by different nations, verifiable by multiple entities, and stored in a manner such that no one can tamper with their authenticity (e.g. one person cannot have more than one passport of the same nationality).
The same way, decentralized identities will require appropriate standards that allow them to be fully acceptable and utilized by different institutions.
Efforts are being made by large institutions, such as W3C and DIF, to establish grounds for such standards.
Interoperability
Similar to standardization, an important issue that faces DID adoption is interoperability, or the ability to achieve communication across two or more blockchains.
When issuing a DID for general use, you probably intend on using it to prove your uniqueness and liveness across multiple platforms (e.g. NFT marketplaces, DAOs), however, if blockchain distributed ledgers are not interoperable with each other, then users will need to issue different DIDs for different platforms, and may even need to have a different wallet for each DID, and struggle with vendor lock-in.
To ensure interoperability, DID issuing entities need to build their infrastructure on a blockchain that supports cross-chain communication and safe data transfer.
How does Fractal ID tackle these challenges?
To tackle the challenges of interoperability, Fractal ID leverages the Substrate framework to deploy our protocol and DID infrastructure. Substrate-based blockchains can be integrated as parachains, enabling them to gain interoperability with other parachains as well as other independent blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. Interoperability lies on Cross-Conesnsus Messages (XCM), in which Cross-Chain Message Passing (XCMP) plays a significant role. XCMP enables parachains to share trusted logic on the same relay chain, for example, transferring tokens between networks, without any additional trust assumptions.
As explained by our protocol developer in the detailed guide, we chose to use Substrate to build our blockchain primarily because it:
- Is built on the Rust programming language
- Is open source, like Fractal ID Protocol
- Has an easy API for common code
- Is fully-featured, meaning that it handles all aspects of a blockchain
In terms of verifying credentials, Fractal ID Wallet allows users of Fractal ID to manage their credentials. Users upload their information to Fractal ID website (e.g. passport, proof of residency) where it is verified by Fractal, encrypted, and stored securely. Whenever a user is required to verify their information — for example, they need to be KYCed to take part in an IDO or participate in a token sale — Fractal ID will issue the required credentials which are later stored on their Fractal ID Wallet and users can share them with the requesting platform.
This way, users can avoid sharing unnecessary data and waiting for KYC processes to take place by the platform they want to use. This allows for a KYC/AML process as easy as connecting a cryptocurrency wallet to a website or exchange, and provides users with the ability to reuse their issued credentials across multiple platforms.
To explore how Fractal ID processes your data and which regulations we abide by, read our privacy policy.
